Bay Area SCAN weekly update 4/6/23
This blog post describes data collected at 8 wastewater treatment plants in the Greater Bay Area of San Francisco, CA, including Sacramento, that are partners in the SCAN project which began in late 2020.
All samples picked up by the couriers as of 4/4/23 have been processed and their data are on the site: wbe.stanford.edu. The data from the SCAN sites are also on data.wastewaterscan.org. If you notice any bugs on the new site or have any comments about it, please email Amanda Bidwell at albidwel@stanford.edu.
COVID-19
SARS-CoV-2 and Variants
SARS-CoV-2 N gene concentrations at SCAN sites are similar to what they were two weeks ago. Concentrations are approximately between 100,000 copies per gram and 500,000 copies/g, still well above our lower detection limit of approximately 1,000 copies/g. Below is a chart showing data from the Southeast plant in San Francisco showing similar concentrations in the N gene concentration (blue line) relative to two weeks ago.
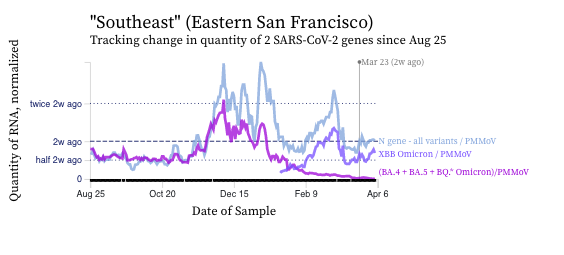
The chart shows that the mutation marker for XBB* (shown in violet) is closer to the blue line (showing the N gene, present in all variants) than the bright purple line (showing the mutation present in the BQ* and BA.5 sublineages). This indicates that most of the individuals shedding SARS-CoV-2 in the sewersheds are likely infected with and shedding XBB* rather than an other variant. We see the pattern across all the sewersheds in SCAN. The assay we use for XBB* will also detect XBB.1.16* as well as XBB.1.9* which are emerging XBB*.
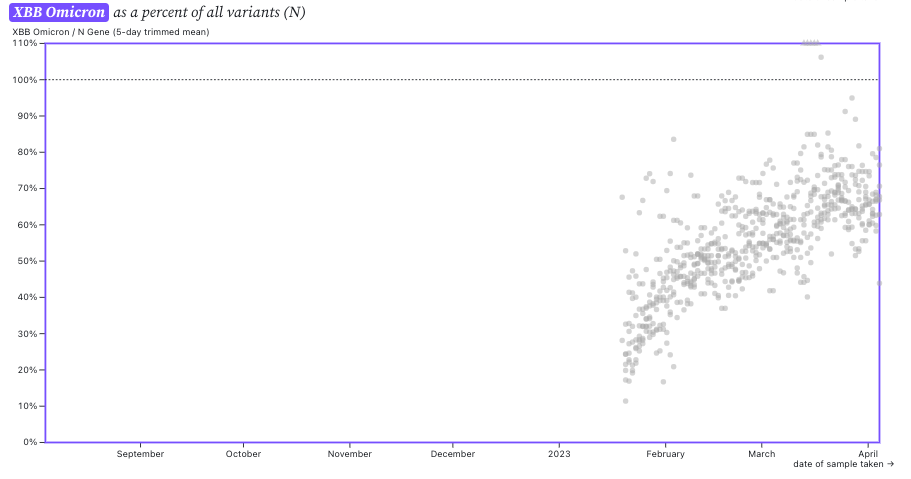
The ratio of the XBB* mutations/N across SCAN plants is shown in the chart below. As the ratio reaches 100%, it suggests that all the SARS-CoV-2 genomes in wastewater have the XBB* mutations. These data indicate that the regional average ratio XBB* mutations/N is ~75% but some places show levels as high as 80%. These are about the same as last week. These data suggest that the majority of infections across the SCAN communities are caused by XBB*.
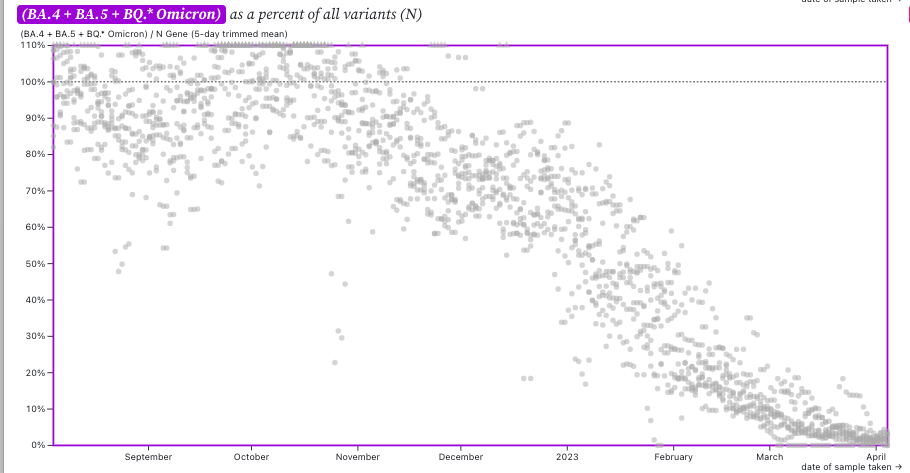
The chart below shows the ratio of the BA.5, BA.4, and BQ* mutation/N across SCAN plants. It can be read the same way as the above chart. The regional average ratio is less than 10% and appears to be bottoming out.
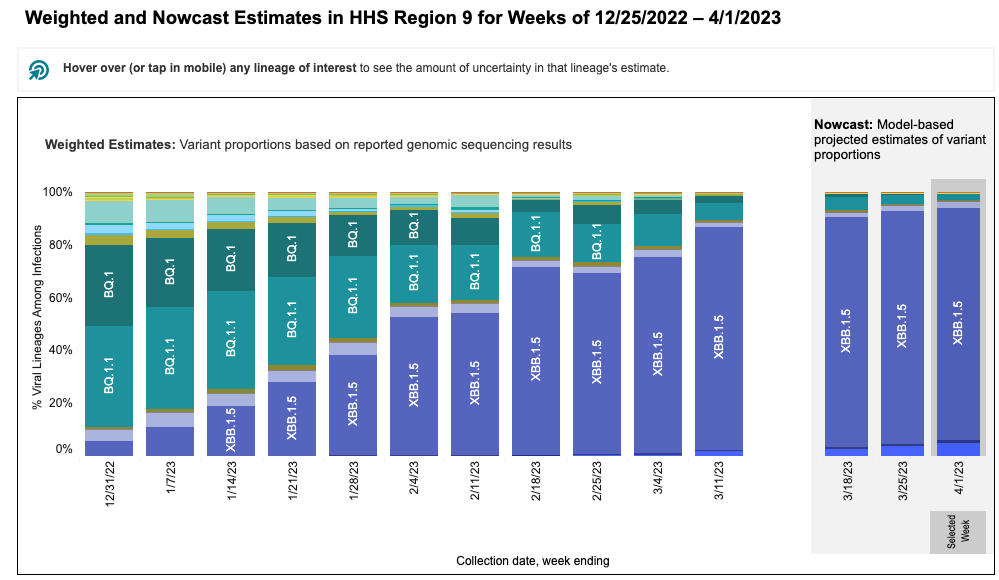
These data from wastewater solids on SARS-CoV-2 variants is consistent with the results from the CDC Nowcast for HHS region 9 (which includes CA). The nowcast suggests nearly all infections in HHS region 9 are caused by XBB* and <5% by BQ* (see screen shot from website below). These model projections for XBB* are higher than what we see in the wastewater. It is important to note that the clinical sample sequencing data used to make the CDC nowcast charts is only available as recently as a month ago (week of 3/11/23 in the chart below) and the rest of the data are model-based predictions.
Other Respiratory Viruses
IAV, IBV, RSV, and HMPV
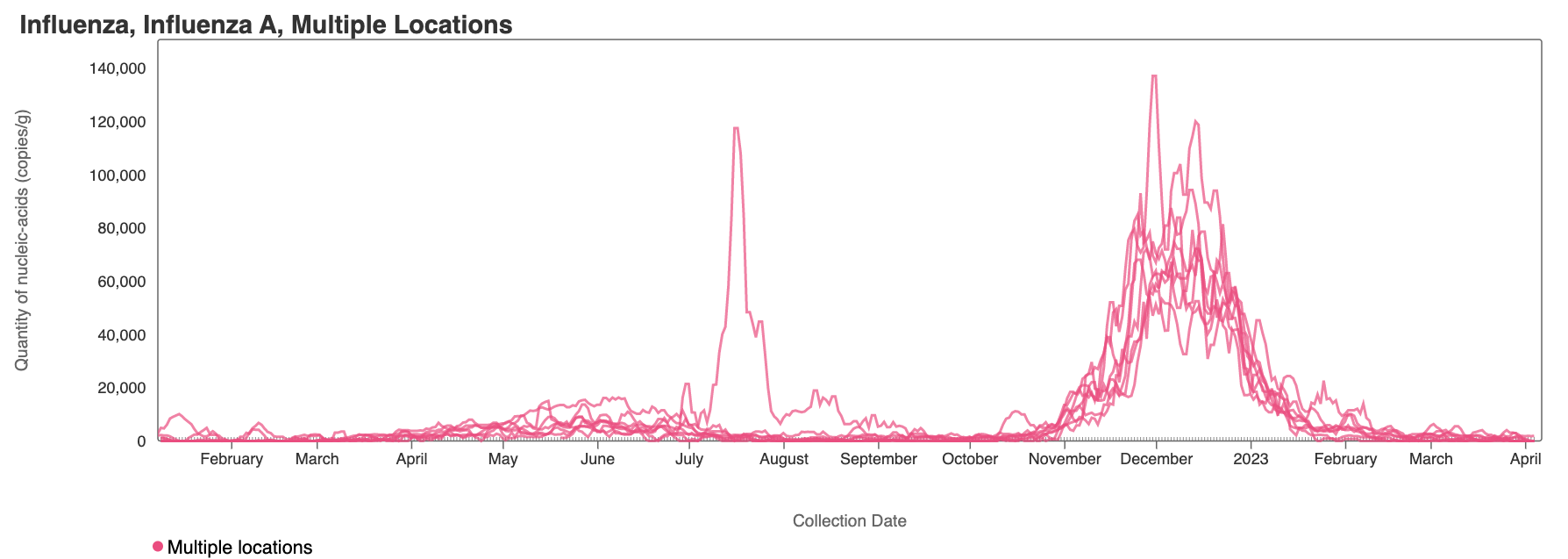
Influenza A (IAV) RNA concentrations have dropped across the plants. Concentrations are generally non-detects in samples from recent works. Influenza A RNA appears to no longer be shed into the wastewater in the SCAN plants. The link to the chart is here if you would like to interact with it.
Influenza B (IBV) RNA continues to be sporadically detected at low concentrations at the SCAN plants. Each plant is represented by a row (y-axis), and dates are shown along the x-axis. Blue indicates a non-detect, and darker orange/red is proportional to concentration with the highest values being darkest. A white means no sample was collected. Here is the link to the heat map chart - the linked chart will update automatically as more data are added to the site.

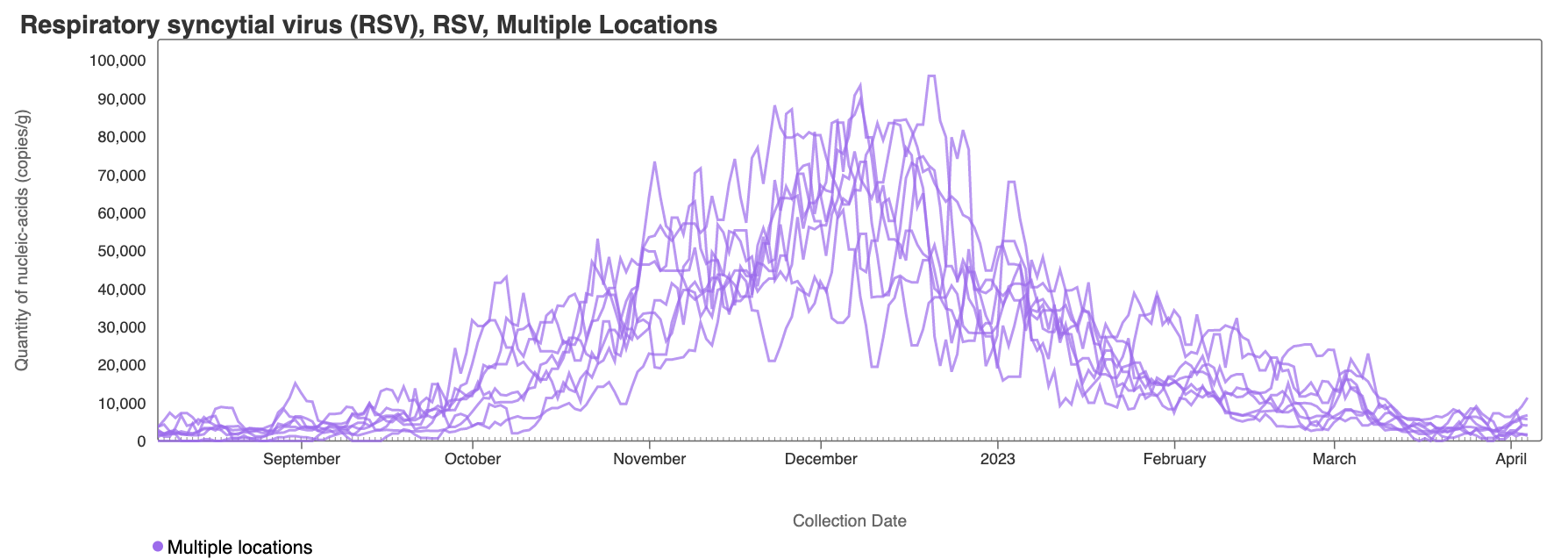
RSV RNA has been non-detectable in some samples from some plants over the last week with some low level detections. This plot shows data from all the SCAN sites together since August 2022 and can be access here. The number of individuals shedding RSV into the wastewater has decreased substantially.
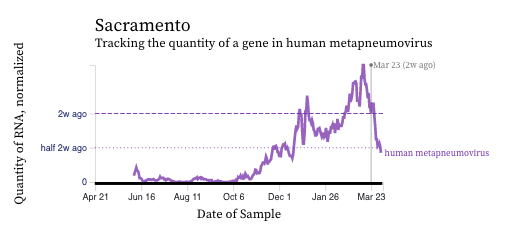
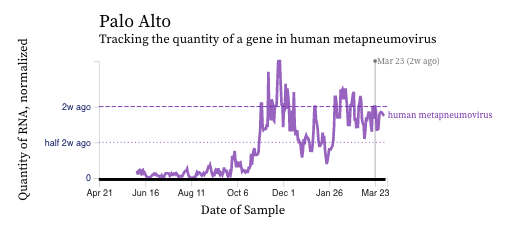
HMPV (human metapneumovirus) RNA concentrations trends are variable across plants. Concentrations are between 10,000 and 100,000 copies/g dry weight. Below are charts showing data from all the SCAN plants together (link here to this chart if you want to interact with it), and just Palo Alto (no trend, relatively high levels), and just Sacramento (decreasing trend, decreasing levels). The pattern here is quite distinct from influenza and RSV and suggests this virus is still circulating in the communities.

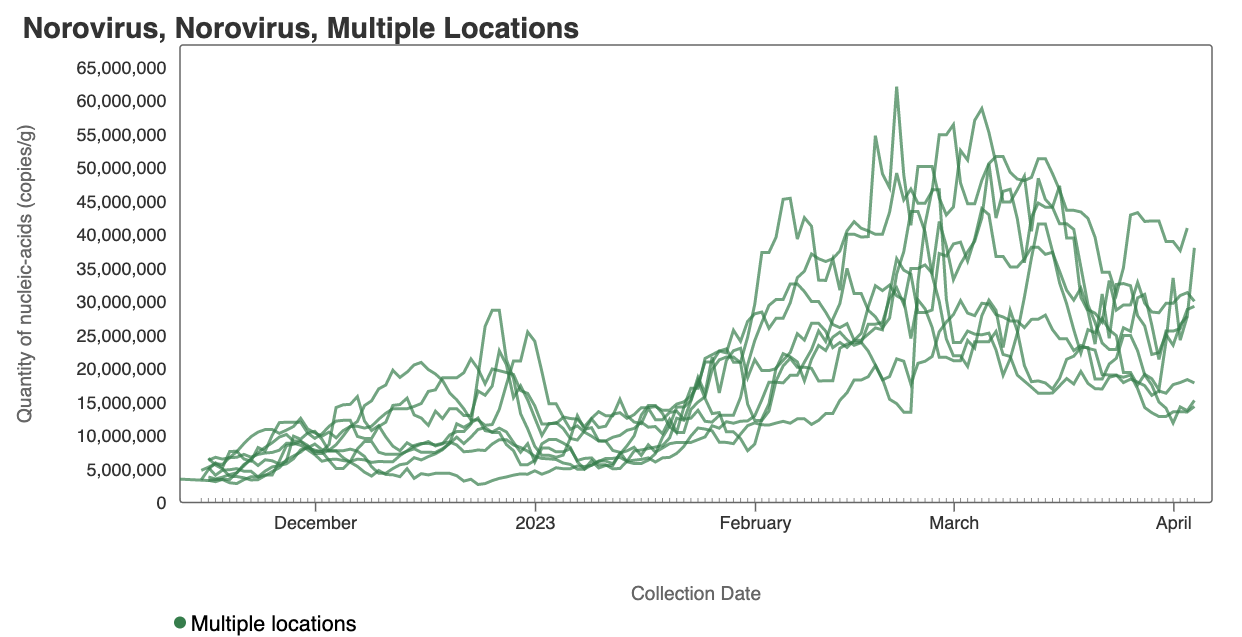
Norovirus
Assay detects human norovirus GII
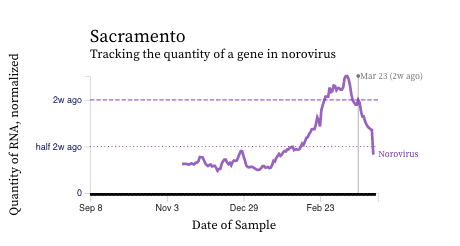
Norovirus GII RNA concentrations have taken a down turn at some plants, but shown recent increases at others. A chart of all the SCAN plants together is shown below, and then just San Jose where we have seen some recent high concentrations, and then just Sacramento where concentrations have begun to decrease. You can interact with the chart of all the plants at this link.

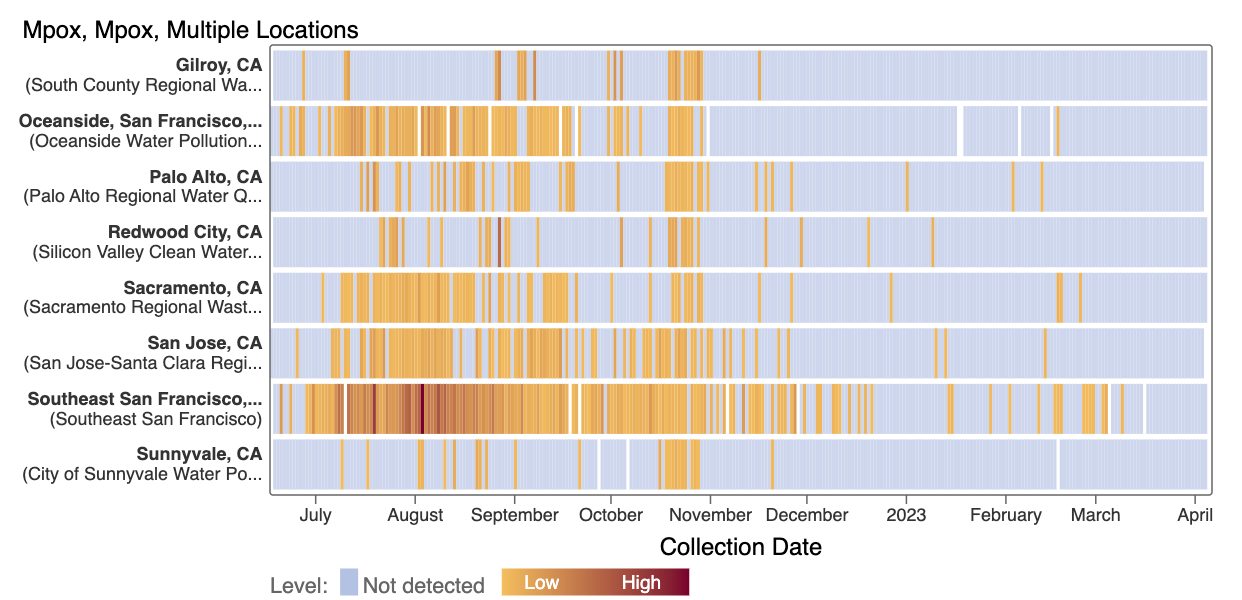
Mpox
We've observed non-detects in the past two weeks for MPXV DNA at the SCAN plants. These heat maps show all the SCAN sites as a row, and each date as a column. The color blue means the sample was non-detect for MPXV DNA and the colors get darker with higher concentrations. The top chart shows just recent data, and the bottom one all the data we have collected, almost a year's worth of data. The charts highlight that we rarely have detections of MPXV DNA at these SCAN plants recently, but we can see how we had much more in the past. You can access this plot here.