Nationwide WWSCAN Update 2/24/23
Hi everyone,
This newsletter contains updates on the WastewaterSCAN program. Below you will find information on the program in terms of participating partners, review of targets being measured, as well as trends in concentrations of infectious disease targets.
Reminder: We officially began using an assay to track a mutation that identifies the SARS-CoV-2 XBB* lineage and ceased tracking using an assay measuring the SARS-CoV-2 S gene as of Monday, February 6, 2023. You can now see XBB* results along with all the data on data.wastewaterscan.org.
Enjoy your weekend,
Ali & Marlene
Participating Plants
141 plants from 26 states are sampling, which represents >10% of the US population
Participants:
- 141 plants sampling
- 145 plants onboarded
- 10.58% US population represented (34,854,825 people)
- 26 states represented
Welcome, New Plants!
- Wheeling, WV
- Bangor, ME
- St. Cloud, MN
- Bridgeton, NJ
- Essex Junction, VT
- Madera, CA

Infectious Disease Target Review
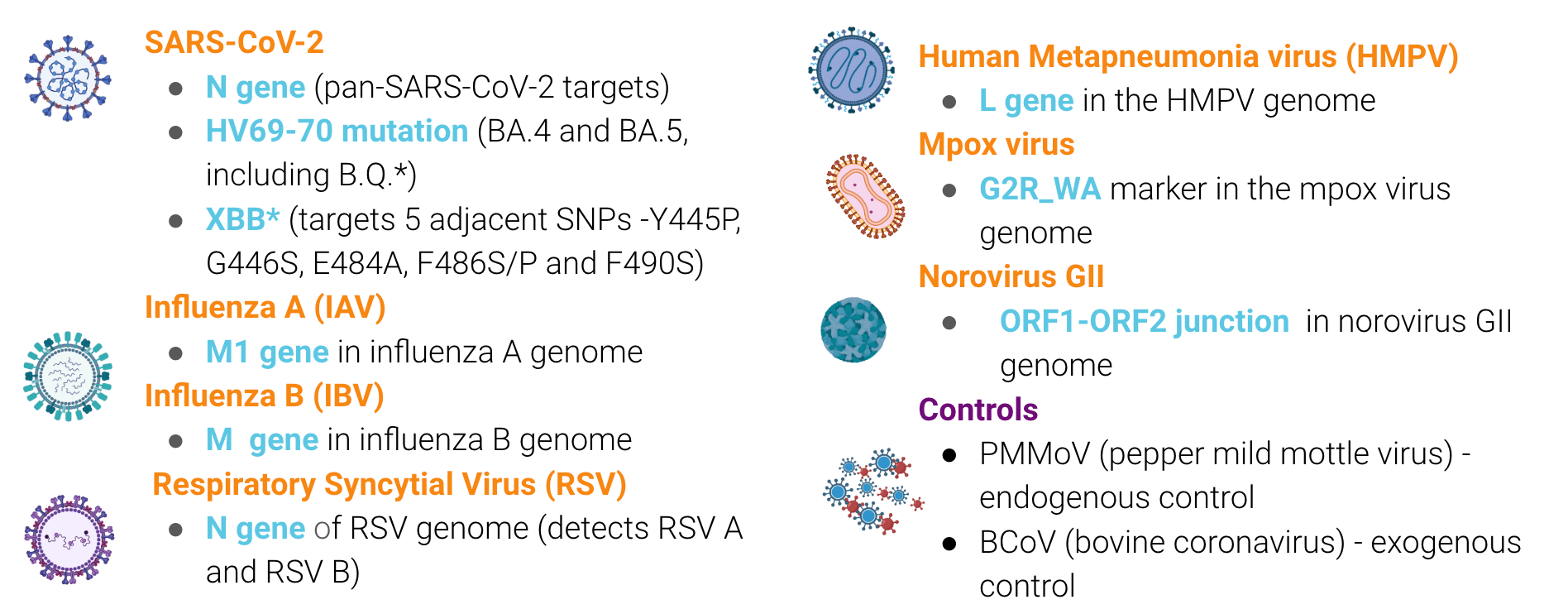
The methods for our assays are in the public domain. You can access them using these QR codes:

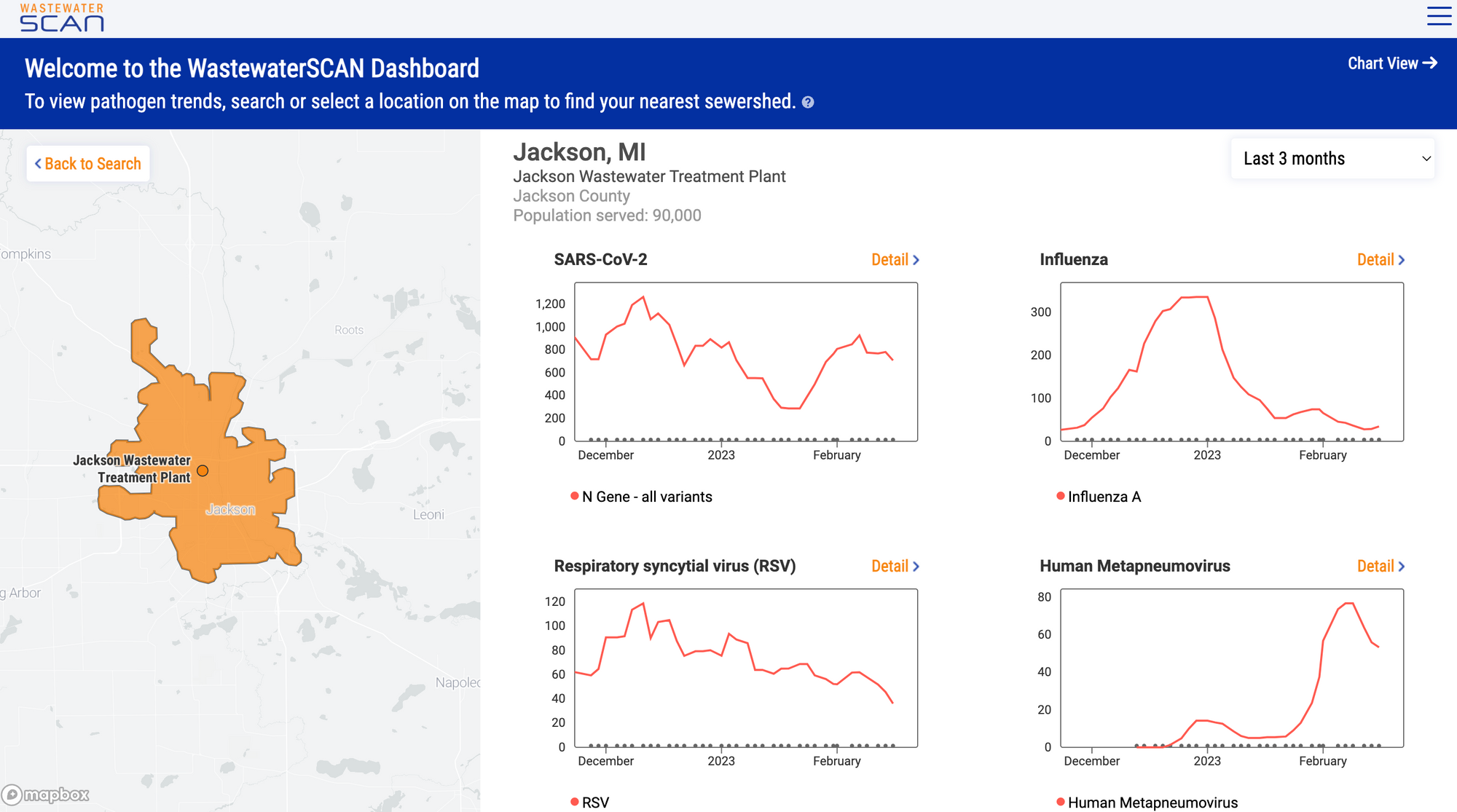
WastewaterSCAN Dashboard
Visit data.wastewaterscan.org to learn more
Our new data platform went live on January 13, 2023. We hope you have been enjoying the new site. For a quick tutorial click the "start here" button at the top right of the chart view page.
SARS-CoV-2 & Variants Trends
21-day nationwide wastewater trends
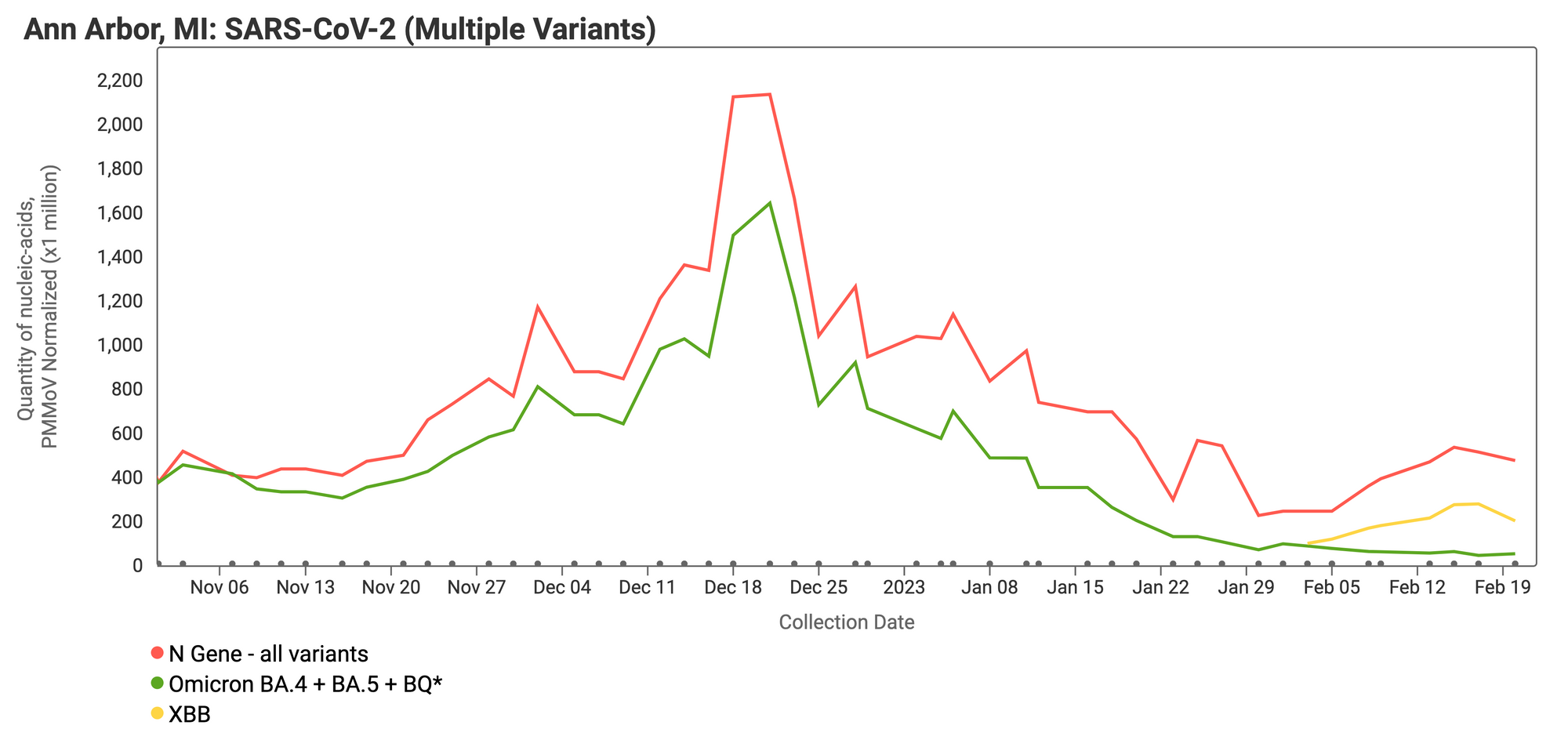
On Monday, February 6, we started testing for XBB* and these results are now available to view by selecting 'SARS-CoV-2 View by Variant' on data.wastewaterscan.org. See an example variant compare plots for Ann Arbor, MI below. The N gene (present in all variants) is shown in red, XBB* mutations are shown in yellow, and the HV69-70 mutation (present in the BA.4, BA.5 and BQ* sublineages) is shown in green. You can see how in the month of February, the yellow line is increasing and is approaching the red line, while the green line is falling off to non-detect. This can be interpreted to mean that more of the SARS-CoV-2 genomes in wastewater solids from this site have the XBB* mutations than the mutation characteristic of the BA.4, BA.5, and BQ* variants. This is consistent with what we know from recent sequencing of clinical specimens, which is that XBB* (and XBB1.5 in particular) is replacing other variants.
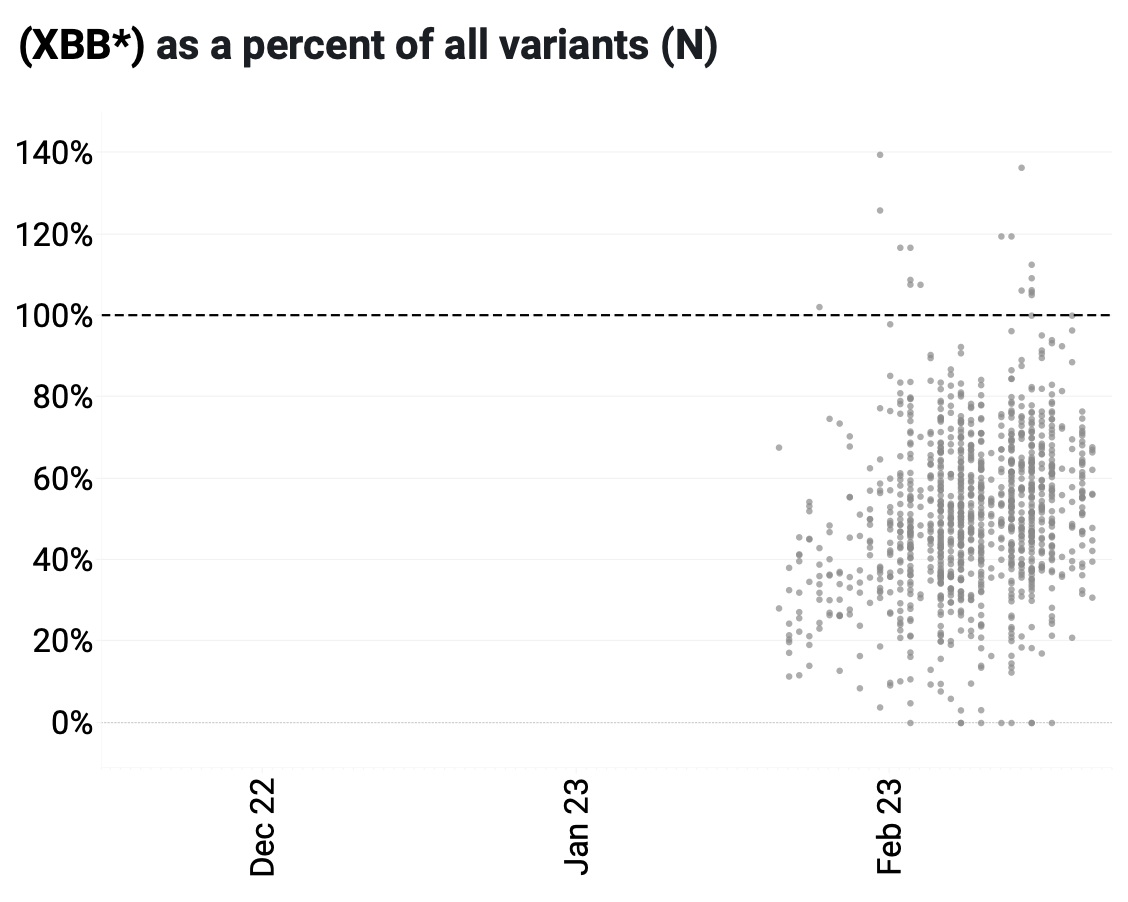
The ratio of the XBB* mutations/N across WWSCAN plants is shown in the chart below. As the ratio reaches 100%, it suggests that all the SARS-CoV-2 genomes in wastewater have the XBB* mutations. These data indicate that the average ratio XBB* mutations/N is ~50% but some places show levels as high as 70-90%, and there is an increasing trend. This suggests 50%-70% of infections across the communities are caused by XBB or XBB1.5 and the percentage is increasing.
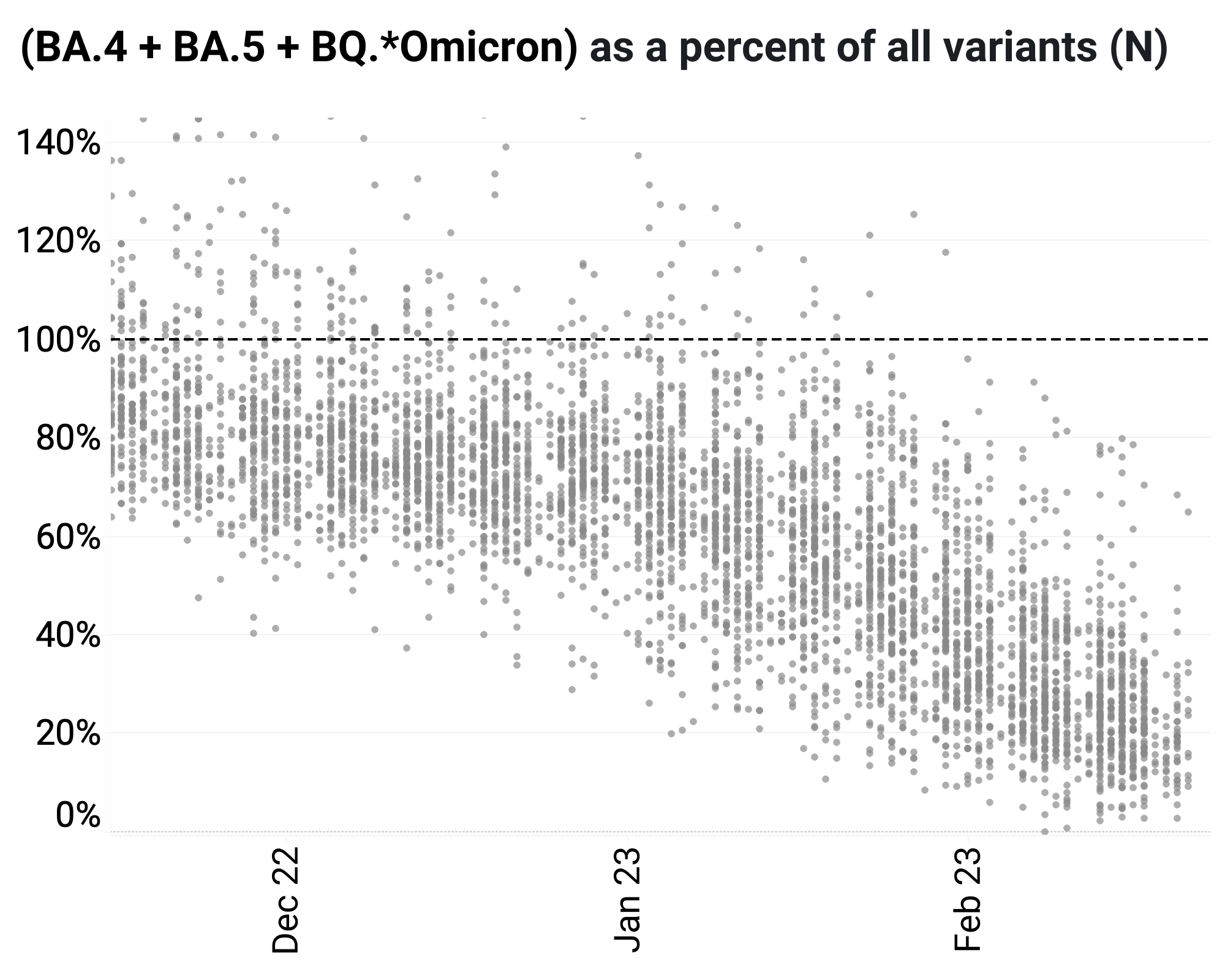
The chart below shows the ratio of the BA.5, BA.4, and BQ* mutation/N across WWSCAN plants. It can be read the same way as the above chart. The average ratio is about 20-30% and has a decreasing trend.
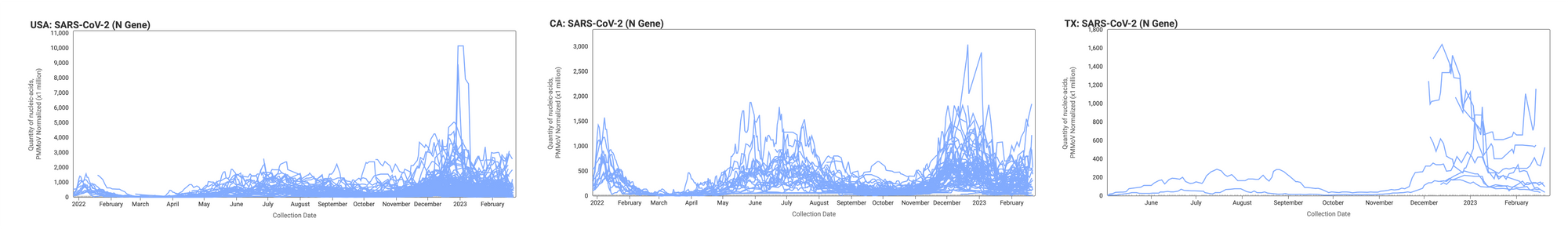
Below are the concentrations (normalized by PMMoV) from all participating sites across the country (left panel), those in California (middle panel), and those in Texas (right panel). The lines you see represent 5-point trimmed averages.
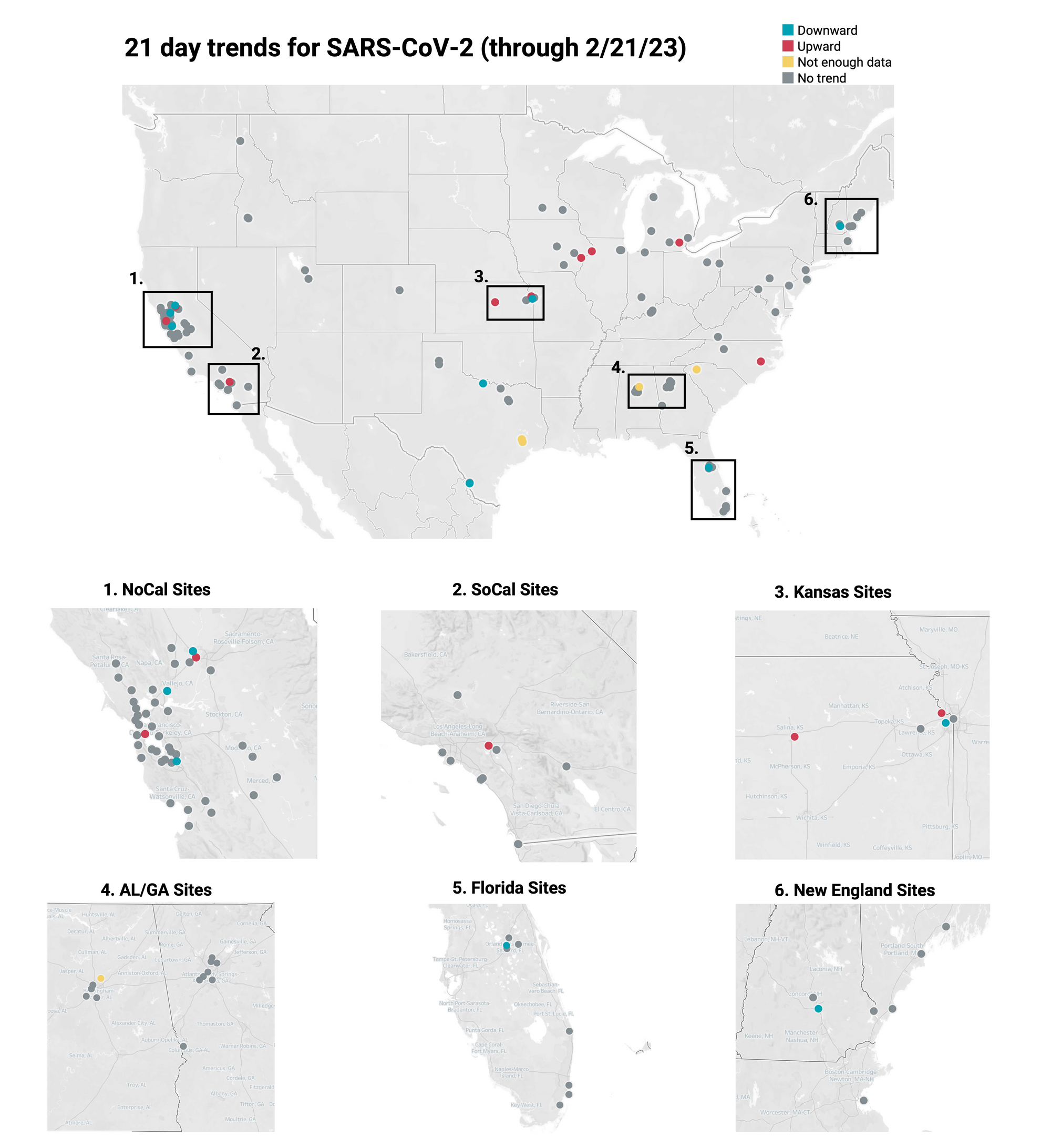
Below is the trend analysis for the SARS-CoV-2 RNA concentrations (N gene concentrations normalized by PMMoV) in wastewater solids at all participating plants. Red indicates a significant upward trend, blue is a significant downward trend, and dark grey is no trend. Yellow indicates that there were not enough data points to calculate a trend. You can read about our methods for trend analysis here. In short, we test for linear trends between log10-transformed concentration (target/PMMoV) and time; the trend must be classified as statistically significant (p<0.1). Of the 141 sites, 9 show an upward trend, 119 show no trend, and 8 show a decreasing trend. The remaining 5 do not have enough data to calculate a trend. This can be interpreted to mean that over the last 21 days, that concentrations of SARS-CoV-2 have generally not changed at most sites.
Influenza Trends
21-day nationwide wastewater trends
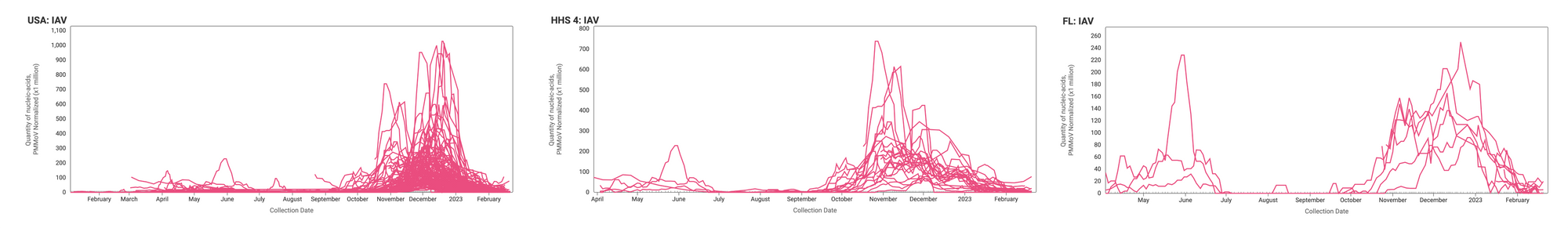
IAV RNA concentrations (normalized by PMMoV) are generally lower now than they were at the height of Influenza A cases earlier this winter at most sites. The median concentration across all sites over the last 21 days is 0 copies/gram. Examples below are from all participating sites across the country (left panel), HHS region 4 - representing the Southeast (middle panel), and Florida (right panel).
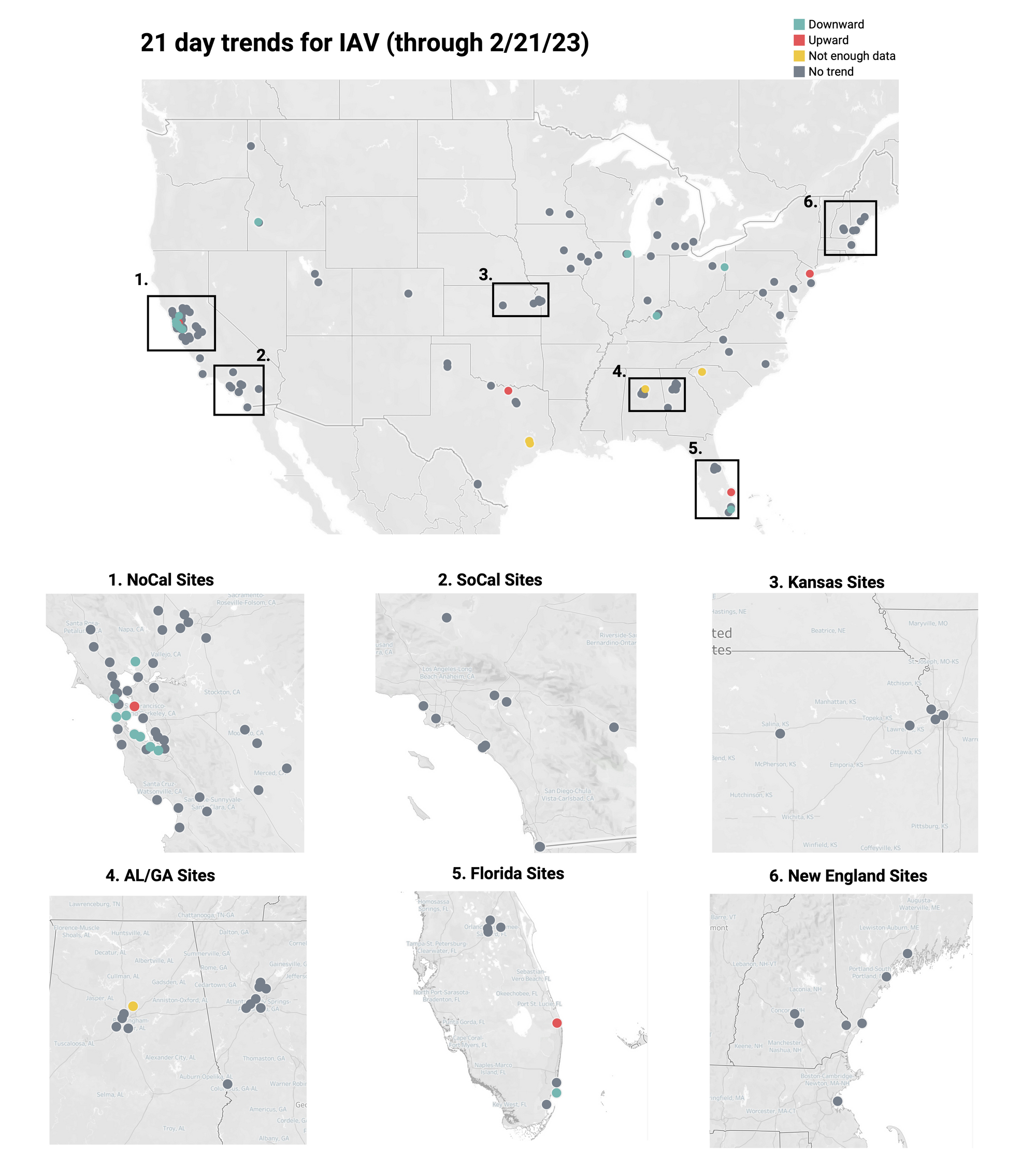
Below is the trend analysis for the IAV RNA concentrations (normalized by PMMoV) in wastewater solids at all participating plants. Red indicates a significant upward trend, blue is a significant downward trend, and dark grey is no trend. Yellow indicates that there were not enough data points to calculate a trend. Of the 141 sites, 4 shows an upward trend, 119 show no trend, and 13 show a decreasing trend. The remaining 5 do not have enough data to calculate a trend.
IBV RNA concentrations (normalized by PMMoV) are mostly non-detect at WWSCAN sites. There have only been 112 positive samples out of 1,115 samples during the past 21 days.
RSV Trends
21-day nationwide wastewater trends
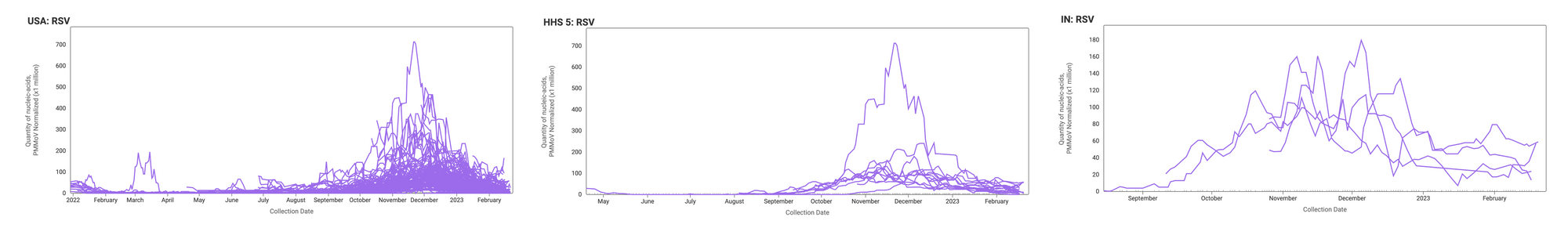
RSV RNA is still detectable in wastewater solids at participating sites, suggesting continued inputs into the wastewater system by RSV shedders. The median concentration across all sites over the last 21 days is 7,871 copies/gram. Examples below are from all participating sites across the country (left panel), HHS region 5 - representing the Midwest (middle panel), and Indiana (right panel).
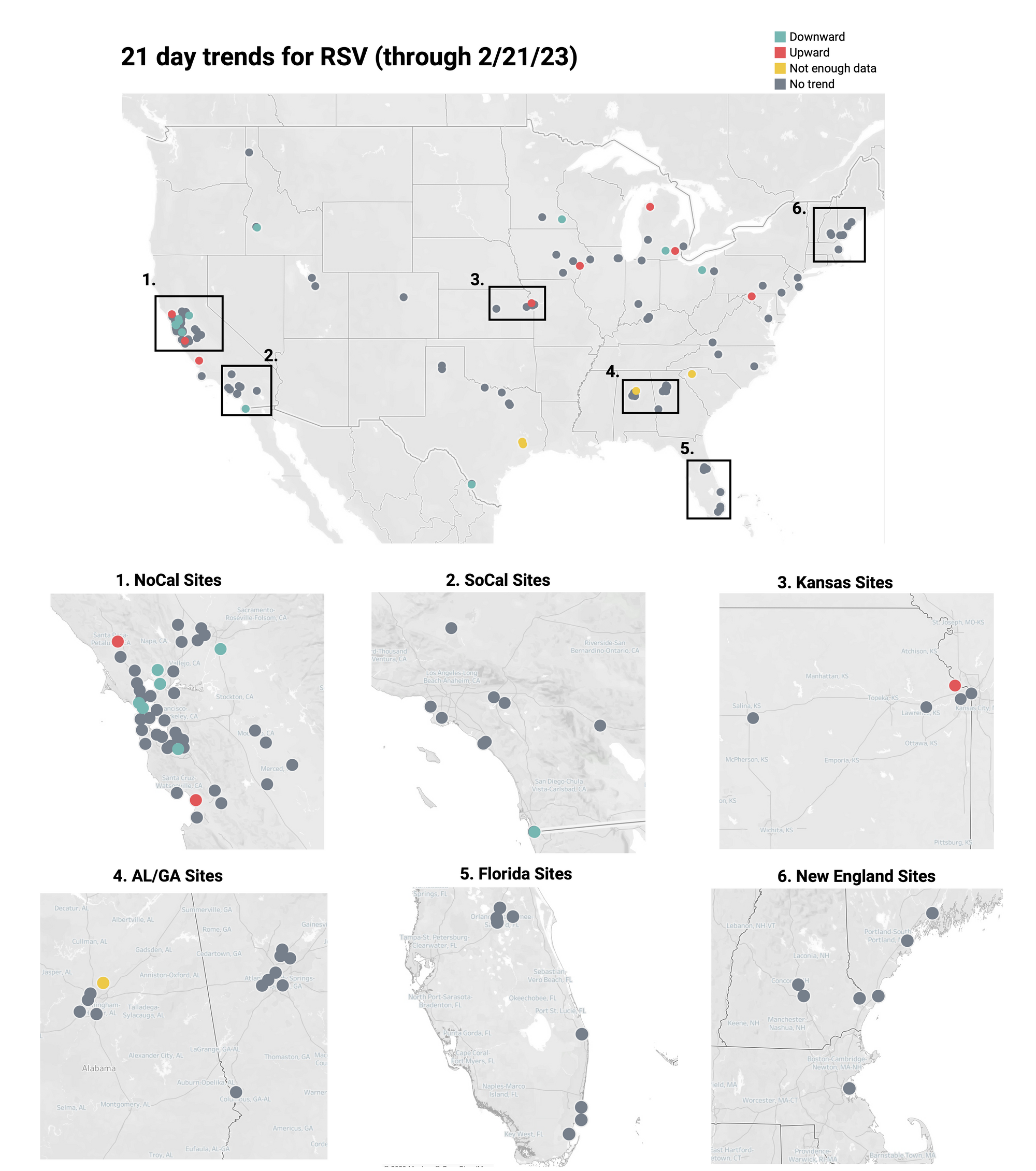
Below is the trend analysis for the RSV RNA concentrations (normalized by PMMoV) in wastewater solids at all participating plants. Red indicates a significant upward trend, blue is a significant downward trend, and dark grey is no trend. Yellow indicates that there were not enough data points to calculate a trend. Of the 141 sites, 8 show an upward trend, 116 show no trend, and 12 show a decreasing trend. The remaining 5 do not have enough data to calculate a trend.
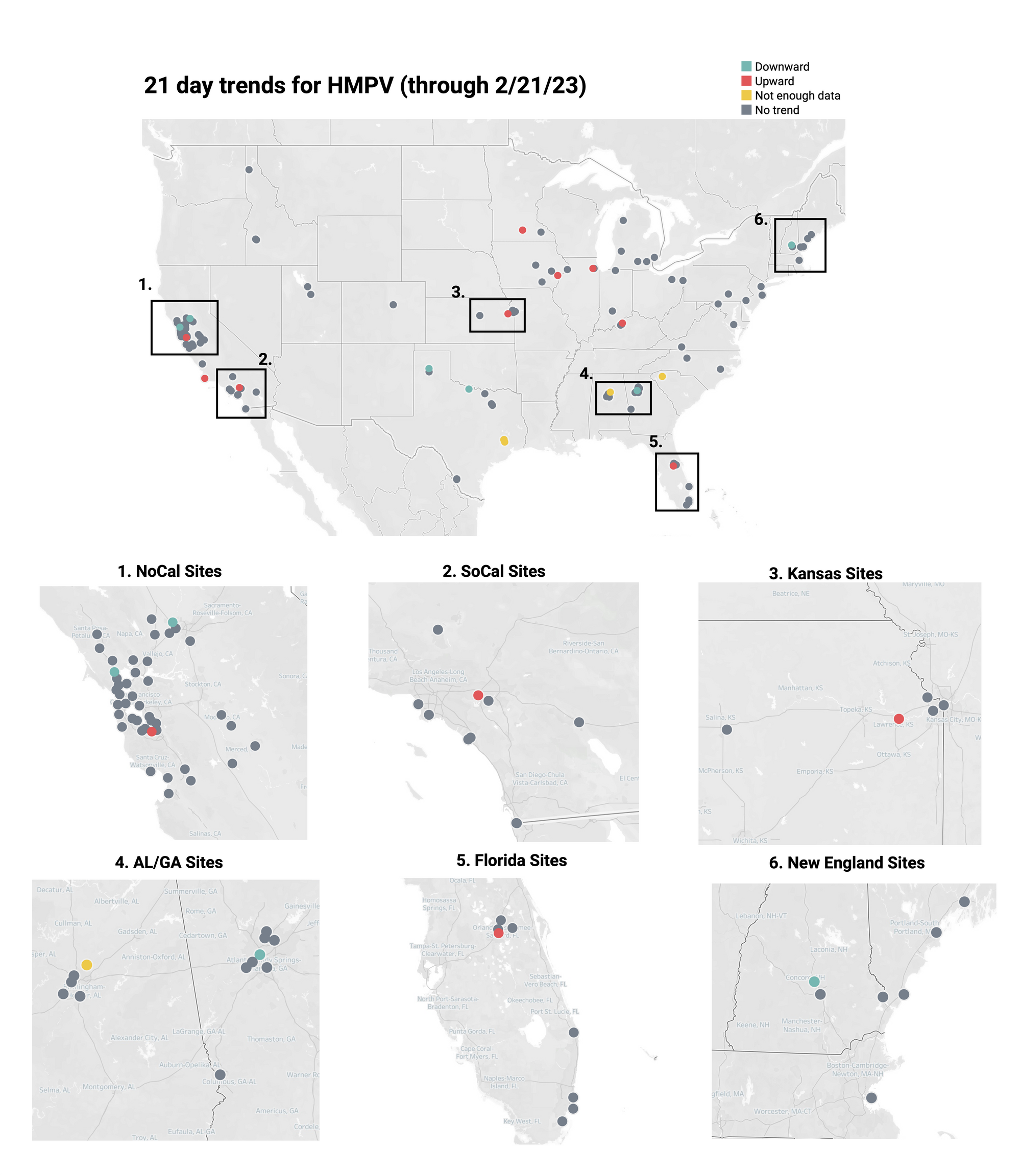
HMPV Trends
21-day nationwide wastewater trends
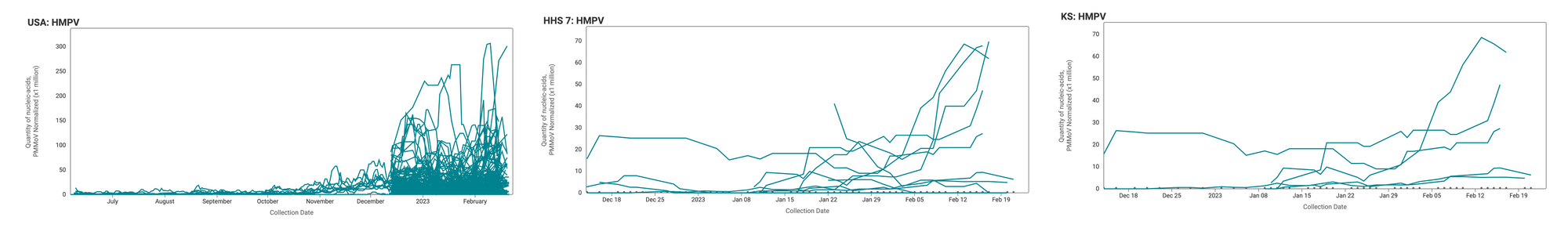
HMPV RNA is consistently detected at the sites. The median concentration across all sites over the last 21 days is 13,200 copies/gram. Examples below show HMPV RNA (normalized by PMMoV) at participating sites across the country (left panel), HHS region 7 (middle panel), and Kansas (right panel).
Below is the trend analysis for the HMPV RNA concentrations (normalized by PMMoV) in wastewater solids at all participating plants. Red indicates a significant upward trend, blue is a significant downward trend, and dark grey is no trend. Yellow indicates that there were not enough data points to calculate a trend. Of the 141 sites, 9 show an upward trend, 121 show no trend, and 6 show a decreasing trend. The remaining 5 do not have enough data to calculate a trend.
HuNoV Trends
21-day nationwide wastewater trends
Norovirus GII RNA has been consistently detected at the sites. The median concentration across all sites over the last 21 days is 20,460,054 copies/gram. Example charts showing concentrations (normalized by PMMoV) in wastewater solids below are from all participating sites across the country (left panel), Michigan (middle panel), and Texas (right panel). In these charts, we show the raw data (HuNoV RNA / PMMoV) rather than the trend lines.

Below is the trend analysis for the Norovirus GII RNA concentrations (normalized by PMMoV) in wastewater solids at the plants. Red indicates a significant upward trend, blue is a significant downward trend, and dark grey is no trend. Yellow indicates that there were not enough data points to calculate a trend. Of the 141 sites, 35 show an upward trend, 96 show no trend, and 5 show a decreasing trend. The remaining 5 do not have enough data to calculate a trend.
You can see that at 25% of WWSCAN plants, the concentrations are trending upwards, which is consistent with some anecdotal evidence that there are increasing cases of Norovirus nationwide. There were several news pieces on this last weekend, including one in the NY Times and one on ABC News.

Mpox virus Trends
Detection of Mpox DNA in wastewater solids over past 21-days is rare
We rarely detected mpox DNA in samples from any site over the past three-weeks. Below you can see, in red, there have only been 11 positive samples out of 1,115 samples during the past 21 days. Outbreaks seem to be under control, but we will continue to monitor so that public health departments can respond if we see consistent detections and increases in concentrations in any sites.

